A basis for the development of peptide-based drugs to prevent JEV and ZIKV infection
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and Zika virus (ZIKV) are mosquito-borne viruses of the Flavivirus genus that cause viral encephalitis and congenital microcephaly, respectively, in humans, and thus present a risk to global public health. The envelope glycoprotein (E protein) of flaviviruses is a class II viral fusion protein that mediates host cell entry through a series of conformational changes, including association between the stem region and domain II leading to virion-target cell membrane fusion.
In the study led by scientists in the Research Group of HIV Viral Biochemistry in WIV, whether peptides derived from the JEV E protein stem can prevent JEV infection were investigated. Peptides from either helix 1 or 2 showed inhibitory activity against JEV in vitro; one of these—designated P5—had a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 3.9 nM in BHK-21 (baby hamster kidney) cells and protected against JEV infection in a mouse model. Consistent with the high degree of conservation among flavivirus stem sequences, they also found that P5 Inhibited ZIKV infection, with an IC50 at the micro- molar level. Similarly, a peptide from helix 2 of the ZIKV E protein stem blocked ZIKV infection. Moreover, in a type I and II interferon (IFN) receptor-deficient mouse model, P5 was proved to reduce the histopathological damages in brain and testes resulting from ZIKV infection. These findings provide a basis for the development of peptide-based drugs to prevent JEV and ZIKV infection.
Link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166354216306118
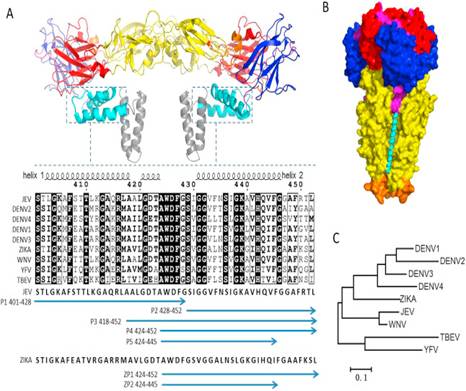
Conformational states of flavivirus E protein and stem sequences. Image by WANG Wei
Contact:
WANG Wei
State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China 430071(http://english.whiov.cas.cn/)