Labeling and imaging with quantum dots (QDs) provides powerful tools to visualize viral infection in living cells. Encapsulating QDs within virions represents a novel strategy for virus labeling.
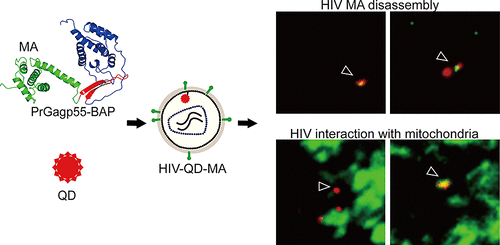
In a present study, the research group led by Prof. CUI Zongqiang in Wuhan Institute of virology of Chinese Academy of sciences developed infectious HIV-1 virions encapsulating QDs through site-specific decoration of the viral matrix protein (MA) and used them to visualize early infection events in human primary macrophages by single-particle imaging.
The MA protein was fused to a biotin acceptor peptide (BAP) tag, biotinylated, complexed with streptavidin-conjugated QDs in live cells, and incorporated into virions during virus assembly. The QD-encapsulated virions were tracked during infection of macrophages at a single particle level. The dynamic dissociation of MA and Vpr was also tracked in real time, and the results demonstrated that MA has multiple dynamic behaviors and functions during virus entry.
More importantly, the scientists tracked the dynamic interplay of QD-encapsulated virions with cellular mitochondria in live primary macrophages. They also found that HIV-1 can induce fission of mitochondria during the early phases of infection.
In summary, they have constructed a type of QD-encapsulated virus particle and used this technology to further our understanding of the early events of HIV-1 infection.
The results have been published in Nano Letters entitled “Encapsulating quantum dots within HIV-1 virions through site-specific decoration of the matrix protein enables single virus tracking inlive primary macrophages”.
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Science Foundation Commission.
Contact:
CUI Zongqiang
E-mail: czq@wh.iov.cn
Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China (http://english.whiov.cas.cn/)